Global Warming: Fact or Fiction? Featuring Physicists Willie Soon and Elliott D. Bloom
Published: August 16, 2019
Is global warming real? Have any such predictions been established scientifically? Would massive “carbon” taxes and other controls put America and the world - especially the poor—at great risk?
At this special event, geoscientist and astrophysicist Willie Soon separates fact from fiction in the global warming debate. He explains why the forecasts from CO2 climate models have been so wrong and why solar influences on clouds, oceans, and wind drive climate change, not CO2 emissions. Stanford University physicist Elliott Bloom then comments.
“The whole point of science is to question accepted dogmas. For that reason, I respect Willie Soon as a good scientist and a courageous citizen.” - Freeman J. Dyson, Professor Emeritus of Physics, Institute for Advanced Study; Templeton Prize Laureate
“I am writing to express my deep admiration and respect for Dr. Willie Soon, a fine astrophysicist and human being.... As Willie has shown in many ways, observational facts do not fit the CO2 dogma, and an enormous amount of evidence points to the Sun as a much more important driver of climate.... Willie was right—whatever the cause of changing temperature, the main driver cannot be the concentration of atmospheric CO2.” - William Happer, Chairman, Presidential Committee on Climate Security; Cyrus Fogg Brackett Professor of Physics Emeritus, Princeton University; Member, National Academy of Sciences
Willie Soon is a geophysicist at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. He received his Ph.D. (with distinction) in aeronautical engineering from the University of Southern California, and he has been Astronomer at the Mount Wilson Observatory; Senior Scientist at the George C. Marshall Institute; Senior Visiting Fellow at the State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science at Xiamen University; and Professor of Environmental Studies at the University of Putra Malaysia. The author of 90 scientific papers, he has IEEE received the Nuclear & Plasma Sciences Society Award, Rockwell Dennis Hunt Award, Smithsonian Institution Award, Courage in Defense of Science Award, Petr Beckmann Award for Courage and Achievement in Defense of Scientific Truth and Freedom, and Frederick Seitz Memorial Award.
Elliott D. Bloom is Professor Emeritus in the Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC) at Stanford University and a Fellow of the American Physical Society. He was a member of the SLAC team with Jerome I. Friedman, Henry W. Kendall and Richard E. Taylor who received the Nobel Prize in Physics.
The Independent Institute is a non-profit, non-partisan, public-policy research and educational organization that shapes ideas into profound and lasting impact. The mission of Independent is to boldly advance peaceful, prosperous, and free societies grounded in a commitment to human worth and dignity. Applying independent thinking to issues that matter, the Independent Institute creates transformational ideas for today’s most pressing social and economic challenges. By connecting these ideas with other organizations and networks, Independent seeks to inspire action that can unleash an era of unparalleled human flourishing at home and around the globe. http://www.independent.org/publicatio...
2014 Breaks Heat Record, Challenging Global Warming Skeptics
- By JUSTIN GILLIS - JAN. 16, 2015 - The New York Times
Last year was the hottest on earth since record-keeping began in 1880, scientists reported on Friday, underscoring warnings about the risks of runaway greenhouse gas emissions and undermining claims by climate change contrarians that global warming had somehow stopped.
Extreme heat blanketed Alaska and much of the western United States last year. Records were set across large areas of every inhabited continent. And the ocean surface was unusually warm virtually everywhere except near Antarctica, the scientists said, providing the energy that fueled damaging Pacific storms.
In the annals of climatology, 2014 surpassed 2010 as the warmest year. The 10 warmest years have all occurred since 1997, a reflection of the relentless planetary warming that scientists say is a consequence of human activity and poses profound long-term risks to civilization and nature.
“Climate change is perhaps the major challenge of our generation,” said Michael H. Freilich, director of earth sciences at NASA, one of the agencies that track global temperatures.
Of the large land areas where many people live, only the eastern portion of the United States recorded below-average temperatures in 2014, in sharp contrast to the unusual heat in the West. Some experts think the weather pattern that produced those American extremes is an indirect consequence of the release of greenhouse gases, though that is not proven.
Several scientists said the most remarkable thing about the 2014 record was that it had occurred in a year that did not feature a strong El Niño, a large-scale weather pattern in which the Pacific Ocean pumps an enormous amount of heat into the atmosphere.
Skeptics of climate change have long argued that global warming stopped around 1998, when an unusually powerful El Niño produced the hottest year of the 20th century. Some politicians in Washington have seized on that claim to justify inaction on emissions.
But the temperature of 1998 is now being surpassed every four or five years, and 2014 was the first time that happened without a significant El Niño. Gavin A. Schmidt, head of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in Manhattan, said the next strong El Niño would probably rout all temperature records.
“Obviously, a single year, even if it is a record, cannot tell us much about climate trends,” said Stefan Rahmstorf, head of earth system analysis at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany. “However, the fact that the warmest years on record are 2014, 2010 and 2005 clearly indicates that global warming has not ‘stopped in 1998,’ as some like to falsely claim.”
Such claims are unlikely to go away, though. John R. Christy, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Alabama in Huntsville who is known for his skepticism about the seriousness of global warming, pointed out in an interview that 2014 had surpassed the other record-warm years by only a few hundredths of a degree, well within the error margin of global temperature measurements. “Since the end of the 20th century, the temperature hasn’t done much,” Dr. Christy said. “It’s on this kind of warmish plateau.”
Despite such arguments from a handful of scientists, the vast majority of those who study the climate say the earth is in a long-term warming trend that is profoundly threatening and caused almost entirely by human activity.
The Warmest Year on Record
Parts of the eastern United States were cooler than average last year, but globally 2014 was the warmest year in recorded history.
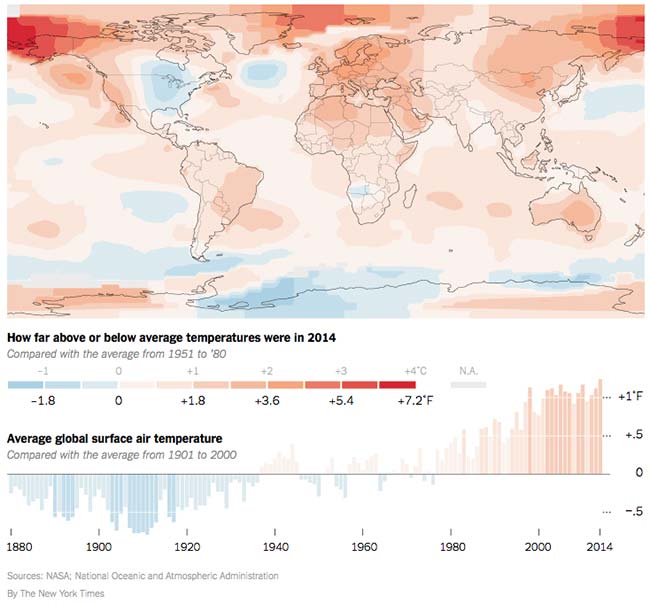
They expect the heat to get much worse over coming decades, but already it is killing forests around the world, driving plants and animals to extinction, melting land ice and causing the seas to rise at an accelerating pace.
“It is exceptionally unlikely that we would be witnessing a record year of warmth, during a record-warm decade, during a several decades-long period of warmth that appears to be unrivaled for more than a thousand years, were it not for the rising levels of planet-warming gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels,” Michael E. Mann, a climate scientist at the Pennsylvania State University, said in an email.
NASA and the other American agency that maintains long-term temperature records, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, issued separate data compilations on Friday that confirmed the 2014 record. A Japanese agency had released preliminary information in early January showing 2014 as the warmest year.
One more scientific group, in Britain, that curates the world’s temperature record is scheduled to report in the coming weeks.
Separate temperature measurements taken from satellites do not show 2014 as a record year, although it is close. Several scientists said the satellite readings reflected temperatures in the atmosphere, not at the earth’s surface, so it was not surprising that they would differ slightly from the ground and ocean-surface measurements that showed record warmth.

“Why do we keep getting so many record-warm years?” Dr. Schmidt asked in an interview. “It’s because the planet is warming. The basic issue is the long-term trend, and it is not going away.”
February 1985 was the last time global surface temperatures fell below the 20th-century average for a given month, meaning that no one younger than 30 has ever lived through a below-average month. The last full year that was colder than the 20th-century average was 1976.
The contiguous United States set a temperature record in 2012, a year of scorching heat waves and drought. But, mostly because of the unusual chill in the East, 2014 was only the 34th warmest year on record for the lower 48 states.
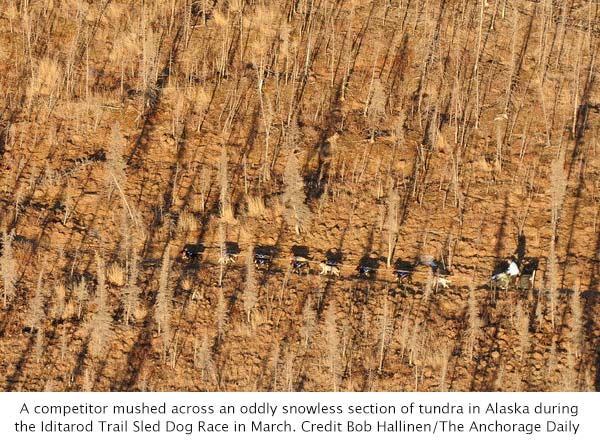
That cold was drawn into the interior of the country by a loop in a current called the jet stream that allowed Arctic air to spill southward. But an offsetting kink allowed unusually warm tropical air to settle over the West, large parts of Alaska and much of the Arctic.
A few recent scientific papers say that such long-lasting kinks in the jet stream have become more likely because global warming is rapidly melting the sea ice in the Arctic, but many leading scientists are not convinced on that point.
Whatever the underlying cause, last year’s extreme warmth in the West meant that Alaska, Arizona, California and Nevada all set temperature records. Some parts of California essentially had no winter last year, with temperatures sometimes running 10 to 15 degrees above normal for the season. The temperature in Anchorage, Alaska’s largest city, never fell below zero in 2014, the first time that has happened in 101 years of record-keeping for the city.
Twenty years of global negotiations aimed at slowing the growth of heat-trapping emissions have yielded little progress. However, 2014 saw signs of large-scale political mobilization on the issue, as more than 300,000 people marched in New York City in September, and tens of thousands more took to the streets in other cities around the world.
The next big attempt at a global climate agreement will come when negotiators from around the world gather in Paris in December. Political activists on climate change wasted no time Friday in citing the 2014 heat record as proof that strong action was needed.
“The steady and now record-breaking rise in average global temperatures is not an issue for another day,” Michael R. Bloomberg, the former New York mayor who is spending tens of millions of dollars of his personal fortune to battle climate change, said in a statement. “It’s a clear and present danger that poses major economic, health, environmental and geopolitical risks.”
Also see: https://venusproject.org/exposed/climate-change-theory.html


